The increased safety type "e" motor and the spark free type "nA" motor are very similar in general structure, and even in terms of test items and inspection requirements, they are quite similar. Many people cannot accurately distinguish the requirements of these two explosion-proof types of motors. Here is a simple comparison in order to stimulate further exploration of these two typesexplosion-proofThe difference between motors.
Explosion proof type definition
“e”Increased safety typeTake additional measures for electrical equipment to improve safety and prevent the possibility of dangerous temperatures, arcs, and sparks under normal operation or specified abnormal conditions.
NA spark free device: a device that structurally minimizes the risk of generating arcs or sparks that can cause ignition under normal usage conditions.
From this perspective, it can be simply said that increased safety motors can prevent arcing and sparks during operation, while the "nA" type, although called spark free, cannot completely prevent and eliminate sparks, but only minimize them to the greatest extent possible. The "nA" device can make the probability of sparks very low, so low that the risk of ignition can reach an acceptable level for people. It is not difficult to understand why the standard stipulates that some increased safety motors (under specific conditions) can reach Gb level, while non sparking motors can only be Gc level.
Comparison of structural and performance requirements
1. Increased safety motors (using current protection devices to prevent exceeding the limit temperature) have requirements for the starting current ratio IA/IN and tE time, which need to be indicated on the motor nameplate. The purpose is to facilitate the selection and configuration of suitable protection devices when using the motor, while spark free motors do not require them.
Both increased safety and non sparking motors have requirements for electrical clearance and creepage distance, but at the same voltage level, the minimum electrical clearance and creepage distance between live parts of increased safety motors are required to be larger than those of non sparking motors (see Table 1 for details), and the material grade of insulation parts used in non sparking motors can be as low as Grade IIIb, while increased safety motors require Grade IIIa or above.
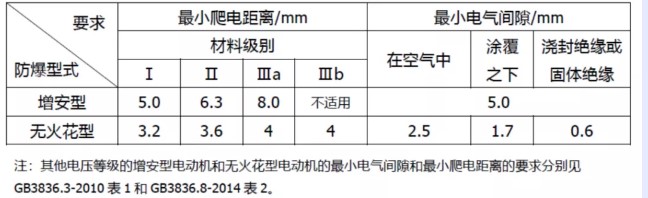
Table 1 Different requirements for creepage distance and electrical clearance between increased safety type and non sparking type when voltage level ≤ 250V
3. For the requirements of squirrel cage rotors, increased safety motors need to be evaluated according to Table 4 of GB3836.3-2010 "Potential Air Gap Spark Hazard Assessment for Squirrel Cage Rotor Ignition Hazard Factors", while for non sparking motors, only motors with rated output greater than 100kW and excluding S1 or S2 working conditions need to be evaluated according to Table 6 of GB3836.8-2014 "Potential Air Gap Spark Hazard Assessment for Squirrel Cage Rotor Ignition Hazard Factors" (see Figure 1 for differences), and then decide whether additional measures need to be taken to ensure that the motor does not ignite during start-up and operation.
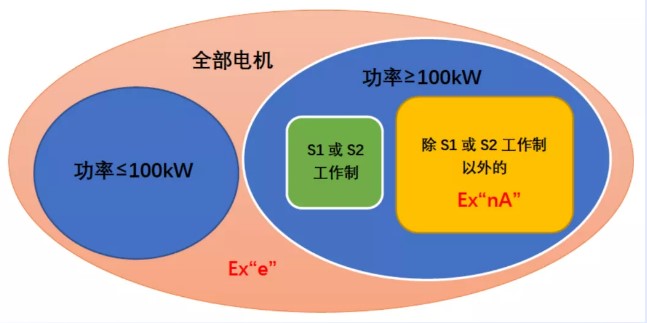
Figure 1 Range of motors requiring air gap spark hazard assessment for increased safety and non sparking types
4. For the requirements of the stator winding insulation system, increased safety motors with a rated voltage exceeding 1kV should have special protective measures to ensure that the casing does not contain explosive gases during start-up, while spark free motors do not have this requirement. It is only recommended to minimize the partial discharge of the high-voltage winding. For windings with a rated voltage ≥ 6.6 kV, it is recommended to use materials that can suppress partial discharge.
Comparison of experimental requirements
All increased safety motors (rated voltage exceeding 1kV) and non sparking motors (Class IIA with loose wound stator rated voltage greater than 1kV or mode wound stator rated voltage greater than 6.6kV, and Class IIB and IIC with rated voltage greater than 1kV) shall undergo steady-state ignition tests of the stator winding insulation system. However, increased safety motors with rated voltage exceeding 1kV shall also undergo transient ignition tests of 10 voltage pulses three times the peak relative ground voltage in a specified explosive gas mixture. Increased safety motors require insulation dielectric strength testing, while spark free motors do not have specific regulations for insulation dielectric strength testing.

|
||||||
|
||||||